Looking to view cron jobs? You’re in the right place! In this blog article, we’ll walk you through a simple solution to effortlessly view your cron jobs. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, we’ve got you covered. So, let’s dive right in and explore how you can easily manage and monitor your cron jobs. Understanding and accessing your cron jobs doesn’t have to be a daunting task anymore. Stay tuned for some valuable insights and practical tips!
View Cron Jobs
Cron jobs, also known as cron tasks, are scheduled tasks that run automatically at specific intervals on a Unix-like system. They are used to automate repetitive tasks such as data backups, system maintenance, and periodic updates. In this article, we will explore how to view cron jobs on your system, providing a comprehensive guide to help you manage and monitor your scheduled tasks effectively.
The Crontab File
To view cron jobs, you need to understand the crontab file. The crontab file is a configuration file that contains instructions for cron to execute specific tasks. Each user on a Unix-like system has their own crontab file, which can be accessed and modified using the crontab command.
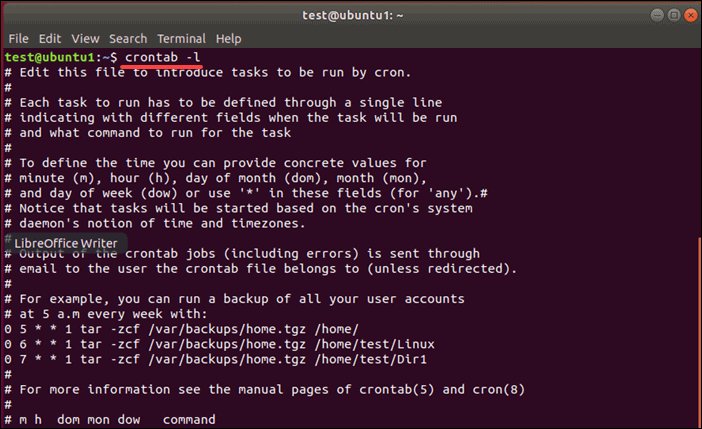
To view the crontab file for your user, simply type the following command in your terminal:
“`
crontab -l
“`
This command will display the contents of your crontab file in the terminal window.
Understanding Cron Job Syntax
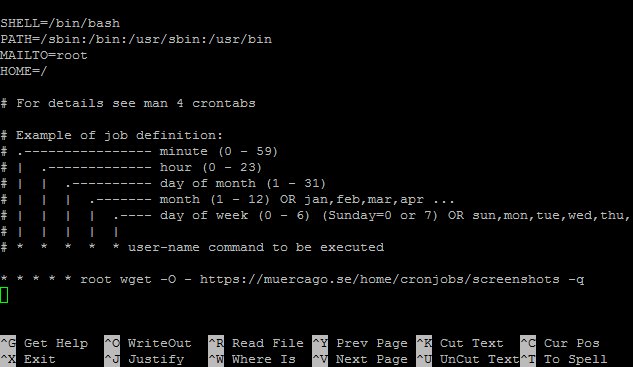
Before diving into viewing cron jobs, it’s crucial to understand the syntax used to define them. Cron job entries consist of six fields, specifying the timing and frequency of the task execution. Here’s a breakdown of the fields in a cron job entry:
1. Minute (0-59)
2. Hour (0-23)
3. Day of the month (1-31)
4. Month (1-12)
5. Day of the week (0-7, where both 0 and 7 represent Sunday)
6. Command to be executed
For example, a cron job entry that runs a script every day at 7:30 AM would look like this:
“`
30 7 * * * /path/to/script.sh
“`
Viewing Cron Jobs with Crontab
The crontab command provides a simple way to view and manage cron jobs. Once you have accessed your crontab file using the `crontab -l` command, you can easily view the existing cron jobs.
The output will display the cron job entries in their defined format. Each line represents a separate cron job, and you can identify the timing and command associated with each task. If you have multiple cron jobs, they will be listed one after another.
Understanding the Output
When viewing cron jobs, it’s important to understand the output and interpret the information correctly. Here are a few key points to keep in mind:
1. The timing information in each line represents when the cron job is scheduled to run.
2. The command following the timing information is the actual task that will be executed.
3. A cron job entry starting with a “#” symbol indicates a comment and does not represent an active task.
By reviewing the output, you can easily identify the execution schedule and the associated commands for each cron job.
Advanced Cron Job Management
While viewing cron jobs with the crontab command provides basic information, you may need more advanced tools for comprehensive management. Here are a few techniques and tools you can use:
1. Modifying Cron Jobs
To modify existing cron jobs, you can use the `-e` option with the crontab command. This option opens the crontab file in an editor, allowing you to make changes to the cron job entries.
For example, to modify the crontab file for your user, simply enter the following command:
“`
crontab -e
“`
This command will open the crontab file in the default editor defined in your system. You can then make the necessary modifications and save the file to update the cron jobs.
2. Logging and Monitoring Cron Jobs
Monitoring the execution and status of cron jobs is essential for ensuring their successful completion. Cron provides logging mechanisms to keep track of job execution.
The system logs cron job execution to a file, which is typically located in the `/var/log` directory. The exact location and naming convention of the cron log file can vary depending on the distribution and configuration of your system.
To view the logs for cron jobs, you can use the `tail` command to display the most recent entries. For example, to view the last 10 lines of the cron log file, use the following command:
“`
tail -n 10 /var/log/cron.log
“`
This command will display the latest entries in the cron log file, allowing you to monitor the execution and troubleshoot any issues with your cron jobs.
3. Cron Job Visualization Tools
If you prefer a more graphical and intuitive approach to managing cron jobs, there are various visualization tools available. These tools provide a user-friendly interface to view, create, modify, and monitor cron jobs.
Some popular cron job visualization tools include:
- cronie: A simple yet powerful tool that allows you to manage cron jobs through a web-based interface.
- Webmin: A comprehensive web-based administration tool that includes a Cron Jobs module for managing scheduled tasks.
- cronview: A command-line tool that visualizes cron jobs in a tabular format, making it easy to review and manage tasks.
These tools can streamline the process of managing cron jobs, particularly for users who prefer a visual approach over the command line.
In this article, we explored how to view cron jobs on a Unix-like system. We started by understanding the crontab file and its role in defining and executing scheduled tasks. Then, we delved into the syntax of cron job entries and learned how to interpret them.
Using the crontab command, we viewed existing cron jobs and examined the output. We also discussed advanced techniques for modifying cron jobs, logging and monitoring their execution, and utilizing cron job visualization tools.
By mastering the art of viewing and managing cron jobs, you can effectively automate repetitive tasks and ensure the smooth operation of your system. So go ahead, dive into your crontab file, and take control of your scheduled tasks. Happy scheduling!
Linux Crash Course – Scheduling Tasks with Cron
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a cron job and how can I view cron jobs?
A cron job is a scheduled task that runs automatically at specified intervals on a Unix-based system. It is commonly used to automate repetitive tasks such as backups, updates, and system maintenance. To view the existing cron jobs on your system, you can use the following command in your terminal:
crontab -lHow can I edit cron jobs?
To edit cron jobs, you need to access the crontab file. You can do this by using the following command:
crontab -eThis will open the crontab file in your default text editor. Make the necessary changes, save the file, and exit the editor. The cron jobs will be automatically updated.
How do I delete a cron job?
To delete a specific cron job, you can use the following command:
crontab -eThis will open the crontab file in your text editor. Simply delete the line corresponding to the cron job you want to remove, save the file, and exit the editor. The cron job will be deleted from the system.
Can I view the output of cron jobs?
By default, the output of cron jobs is sent to the owner of the cron job via email. If you want to view the output directly in the terminal or redirect it to a file, you can modify your cron job command accordingly. For example:
* * * * * /path/to/command >> /path/to/output.log 2>&1This will redirect the output to the specified file, in this case, “output.log”. You can replace “/path/to/output.log” with the desired file path.
How can I check if a cron job is running?
To check if a specific cron job is running, you can use the following command:
pgrep -f "cron_job_name"This will return the process ID (PID) of the running cron job if it is found. If nothing is returned, it means the cron job is not currently running.
Can I view the system-wide cron jobs?
Yes, you can view the system-wide cron jobs by accessing the system’s crontab file. The location of this file may vary depending on the Unix-based system you are using. In most cases, the system crontab file can be found at:
/etc/crontabYou can open this file using a text editor to view the system-wide cron jobs defined on your system. However, make sure to have the necessary permissions to access and modify this file.
Final Thoughts
To view cron jobs, simply access your server’s command line interface and enter the necessary command. Once executed, you will be presented with a list of all scheduled tasks and their corresponding execution times. This allows you to effectively manage and monitor your cron jobs, ensuring they are running as intended. By regularly reviewing this information, you can promptly identify any issues or conflicts, ensuring the smooth execution of your scheduled tasks. Monitoring cron jobs in this way is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of your server’s automated processes.